Draw ray diagrams for the cases of images obtained in concave mirror as
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Are you struggling with how to draw ray diagrams for mirrors? If so, you’re not alone. Many students find this topic challenging, but with the right guidance, you can master this skill and excel in your physics studies.
The Pain Points of Drawing Ray Diagrams for Mirrors
One of the main pain points of drawing ray diagrams for mirrors is understanding the different types of mirrors and their properties. This includes knowing the difference between concave and convex mirrors, and how the position of an object relative to the mirror affects the image produced.
Another pain point is grasping the concept of ray tracing and understanding how to draw accurate and neat diagrams. This requires a clear understanding of the rules for tracing rays and where to place them on the diagram.
How to Draw Ray Diagrams for Mirrors
To draw a ray diagram for a mirror, start by identifying the type of mirror you’re working with. If it’s a concave mirror, identify the center of curvature and the focal point. If it’s a convex mirror, identify the center of curvature and the focal length. Next, identify the object and its position relative to the mirror. Draw a straight line from the object to the mirror, and then draw a second line from the top of the object through the focal point or the center of curvature, depending on the type of mirror. Finally, draw a third line from the top of the object parallel to the principal axis, and extend this line backwards to where it intersects with the other two lines. This point of intersection is where the image will form.
Summary of How to Draw Ray Diagrams for Mirrors
Drawing ray diagrams for mirrors can be challenging, but with some practice, anyone can master this skill. Start by identifying the type of mirror and the position of the object, and then use the rules for ray tracing to draw an accurate diagram that shows where the image will form.
Understanding Concave Mirrors
When working with concave mirrors, it’s important to understand their unique properties. These mirrors are curved inward and can produce both real and virtual images, depending on the position of the object. If the object is located beyond the focal point, a real image will form on the opposite side of the mirror. If the object is located between the focal point and the mirror, a virtual image will form behind the mirror.
When drawing a ray diagram for a concave mirror, the top of the object should always be above the principal axis. The center of curvature and focal point will be located on the opposite side of the mirror from the object, and these points should be labeled on the diagram.
Understanding Convex Mirrors
Convex mirrors are curved outward and always produce virtual images. The image formed is always smaller than the object and located behind the mirror. When drawing a ray diagram for a convex mirror, the top of the object should be below the principal axis, and the focal point and center of curvature will be located on the same side of the mirror as the object.
Tips for Drawing Accurate Ray Diagrams
To draw accurate ray diagrams, it’s important to follow a few simple rules. Always draw rays from the top of the object, and make sure they are straight and parallel to each other. Label the focal point and center of curvature on the diagram, and make sure your lines intersect at the correct point.
Example of Drawing Ray Diagrams for Mirrors
When I was first learning how to draw ray diagrams for mirrors, I struggled with understanding the different types of mirrors and where to place the focal point. However, with some guidance from my teacher, I was able to master this skill and achieve great success in my physics studies.
 Common Questions About How to Draw Ray Diagrams for Mirrors
Common Questions About How to Draw Ray Diagrams for Mirrors
1. What is a ray diagram for a mirror?
A ray diagram for a mirror is a drawing that shows how light rays interact with the mirror to form an image of an object. It can help us understand how an image is formed, and where it is located relative to the mirror.
2. How do you determine the type of mirror when drawing a ray diagram?
When drawing a ray diagram, you can determine the type of mirror by looking at its shape. Convex mirrors are curved outward, while concave mirrors are curved inward.
3. What is the difference between a real and a virtual image?
A real image is formed when light rays converge at a point and can be projected onto a screen, such as a piece of paper. A virtual image is formed when light rays appear to converge at a point, but do not actually converge. Virtual images are always upright and smaller than the object.
4. What is the focal point of a mirror?
The focal point of a mirror is the point at which parallel light rays converge after reflecting off the mirror. It is located halfway between the mirror and the center of curvature.
Conclusion of How to Draw Ray Diagrams for Mirrors
Drawing ray diagrams for mirrors can be challenging, but with some practice, anyone can master this skill. By understanding the different types of mirrors, the properties of each, and following the rules for ray tracing, you can draw accurate and neat diagrams that show where an image will form. With this knowledge, you’ll be well on your way to excelling in your physics studies.
Gallery
My Physics Webschool: 7/17/11 - 7/24/11
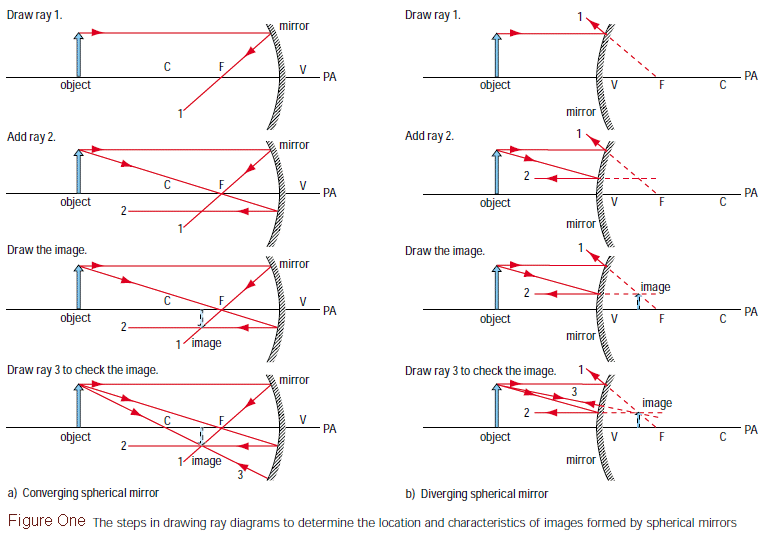
Photo Credit by: bing.com / ray diagram physics focal point gif
Concave Mirror Ray Diagrams - YouTube
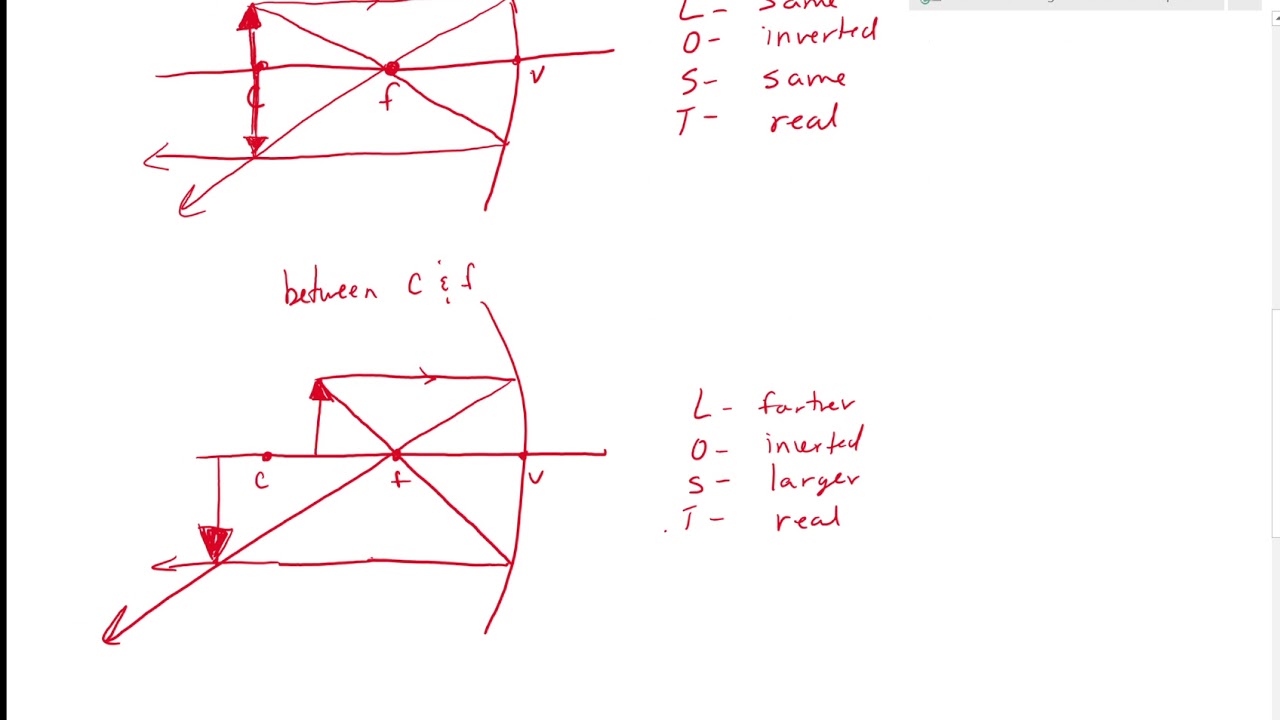
Photo Credit by: bing.com / concave diagrams
Draw Ray Diagrams For The Cases Of Images Obtained In Concave Mirror As

Photo Credit by: bing.com / concave ray mirror diagrams cases draw
How To Draw Ray Diagrams For Convex Mirrors
Photo Credit by: bing.com / mirrors convex involving concave situations multiple
How To Draw Ray Diagrams For Convex Mirrors
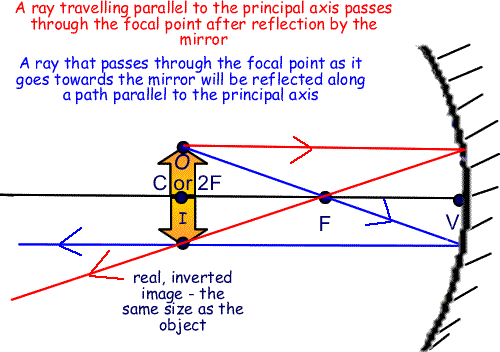
Photo Credit by: bing.com / concave convex diagrams object formed ray5 dekel